In honor of Memorial Day, our Warehouse and Support will be closed Monday, May 27, 2024.

In honor of Memorial Day, our Warehouse and Support will be closed Monday, May 27, 2024.

Portable FID (Flame Ionization Detector), also commonly known as Toxic Vapor Analyzer or TVA*, technology has evolved significantly, and when it comes to choosing the right equipment for Leak Detection and Repair (LDAR), it’s crucial to make an informed decision. Today, we’re comparing two leading portable FIDs: the phx42 and the TVA 2020, to see why the phx42 emerges as the superior choice.
*This is a misnomer, but also a term the industry has accepted to describe portable FIDs.
For professionals regularly using a portable FID, the weight and size of the device are critical. The phx42 weighs a mere 7.25lbs (3.29kg), making it significantly lighter than the TVA 2020, which weighs 9.4lbs (4.26kg). This difference is not just about comfort; it’s about reducing fatigue during long hours of fieldwork. The phx42’s compact dimensions (10 x 2.16 x 7.5 inches or 25.4 x 5.5 x 19 cm) also make it more manageable in confined spaces, a common challenge in field operations.
In the demanding environments where portable FIDs are used, durability is non-negotiable. The phx42’s aluminum case stands out against the TVA 2020’s plastic construction, promising better resilience against the rigors of fieldwork. Moreover, the phx42 comes standard with Bluetooth connectivity, a feature that costs extra with the TVA 2020. This modern necessity enhances data transmission efficiency and aligns with current EPA Consent Decrees.
Performance-wise, the phx42 offers a wider detection range of 0-100,000 ppm compared to the TVA 2020’s 0-50,000 ppm. This broader range allows for more precise and varied measurements. Both devices offer a 10-hour run time, but the phx42 facilitates continuous monitoring, a critical feature for comprehensive area assessments. It also boasts automatic temperature compensation for extreme cold, a feature requiring manual intervention in the TVA 2020.
The phx42 shines in its user-friendly design. It features quicker hydrogen refill times (~15 seconds), an important factor in maintaining operational efficiency. The device also conducts self-checks for machine health, reducing the likelihood of field breakdowns. Additionally, the phx42’s automated shutdown sequence to prevent internal moisture accumulation is a thoughtful feature that prolongs device life.
Cost is a crucial factor in equipment selection, and the phx42 offers significant savings in maintenance and replacement parts. Components like the pump, battery, and charger are more affordable compared to those for the TVA 2020, reducing the total cost of ownership over time.
When evaluating the phx42 against the TVA 2020 for your portable FID needs, the phx42 stands out for its lighter weight, robust construction, advanced features, enhanced performance, ease of maintenance, and cost efficiency. These factors make the phx42 not just a tool, but a reliable partner in the demanding field of LDAR.
For LDAR professionals seeking a portable FID that combines performance, durability, and operational efficiency, the phx42 is an unmatched choice.
We’ll be closed on Monday. If you need assistance over the long weekend to meet a compliance deadline, please call 877-788-1110 ext. 704 and we will do our best to find someone to help you.
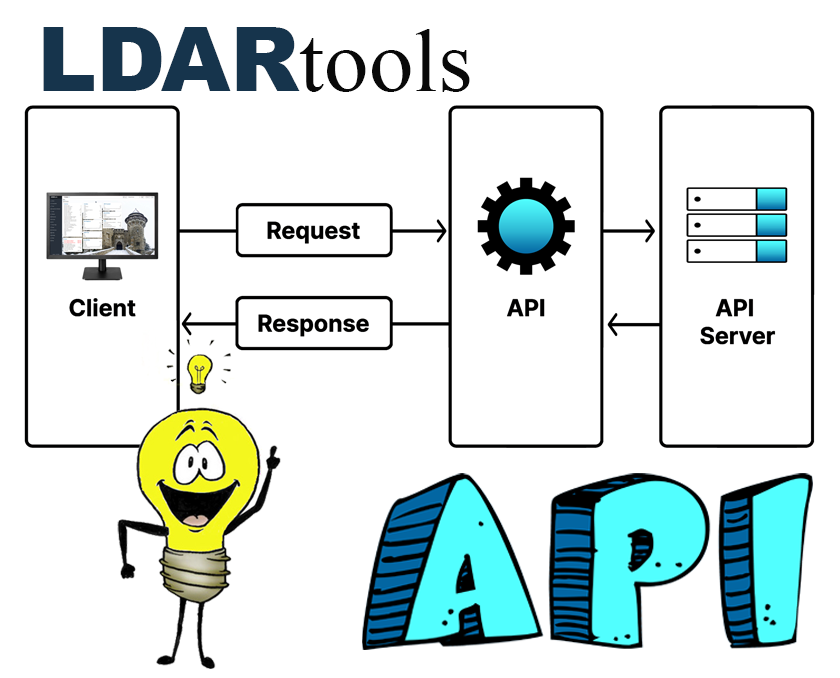
The LDAR Tools API is a powerful tool that can be used to automate and streamline LDAR workflows. The API can be used to perform a variety of tasks, including:
The LDARtools API is RESTful, which means that it uses standard HTTP methods to perform requests. This makes it easy to integrate the API with other applications and services.
To use the API, you will need to create a token. Our Devs would be happy to help with that if you email your request to support@LDARtools.com.
The Chateau API documentation provides detailed information about the API’s endpoints, parameters, and responses. You can find the API documentation on the LDAR Tools website below.
If you are using Chateau, I encourage you to explore the API documentation and learn how you can use it to improve your productivity. The Chateau API is a powerful tool that can help you to automate and streamline your LDAR workflows.
Here are some additional resources that you may find helpful:
The future of leak monitoring in industries is rapidly transforming with state-of-the-art tools and technologies. One such advancement that’s driving accuracy and efficiency in leak detection is the portable Flame Ionization Detector (FID). But using a portable FID requires precise location descriptions to ensure the accuracy of results. Enter Chateau Mobile’s Location Description Builder.
The precision with which a portable FID works depends significantly on the location description provided. An accurate description ensures the detector can pinpoint the exact leak source, making the technician’s job easier and ensuring the integrity of the system being tested.
If your existing Location Description is in the required format, Chateau Mobile allows you to tweak specific elements in the description. For example, you can easily switch from “4 FT WEST” to “6 FT WEST”. However, if your location description doesn’t align with the required format, Chateau Mobile enables you to reconstruct it from the ground up.
Here’s a breakdown of the terms and how they’re applied:
For those leveraging the power of portable FID for leak detection, optimizing location description is paramount. Chateau Mobile’s intuitive Location Description Builder simplifies this task, allowing technicians to work faster and with higher accuracy.
The need for responsible and sustainable operations has never been more critical in our evolving energy landscape. Essential aspects of this responsibility are establishing and maintaining leak rate standards. Learn more about the importance of these regulations.
Leak rate standards dictate the acceptable level of emissions during various industrial processes, particularly in the oil and gas industry. These standards encourage companies in this industry to minimize the release of harmful pollutants and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the atmosphere from equipment leaks. The standards cover different equipment with unique leak rate limits, including valves, pumps, connectors, and flanges.
Various regulatory bodies, such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States or the European Union’s Industrial Emissions Directive, set these limits to ensure industries operate responsibly and contribute to a cleaner environment. The New Source Performance Standards set by the EPA is a prime example of industry-specific leak rate regulations. Alternatively, some businesses set their own standards at or above those recommended by government oversight agencies.
Leak rate standards play a significant role in protecting public health and the environment. Emissions from industrial leaks can contribute to air pollution, which is linked to various health issues, such as respiratory problems, cardiovascular diseases, and even cancer. By adhering to established leak rate standards, energy companies can minimize the release of harmful pollutants and demonstrate their commitment to safeguarding the well-being of surrounding communities.
Compliance with leak rate standards helps energy companies maintain a positive reputation and strong relationships with regulatory bodies, stakeholders, and the general public. Non-compliance often leads to fines, penalties, operational shutdowns, or legal actions that can damage a company’s reputation and erode trust among investors and customers.
Adhering to leak rate standards also yields substantial financial gains for energy companies. By implementing LDAR programs, companies can identify and repair leaks more efficiently, reducing the loss of valuable resources such as natural gas or other chemicals. This can improve operational efficiency, leading to cost savings and increased profits.
By proactively addressing leaks and complying with regulations, companies can avoid costly fines, penalties, legal liabilities, and damaged assets. In some cases, energy companies are eligible for tax incentives or credits for demonstrating exceptional compliance or implementing emission reduction technology.
Establishing and adhering to leak rate standards are important for energy executives and professionals working in refineries and processing facilities. Companies can protect public health, reduce environmental impact, maintain a positive reputation, and reap financial benefits by embracing proper LDAR protocols and practices. Ensure your facility has the ideal leak detection equipment by exploring our selection of FID analyzer devices and related products at LDARtools!

Leak Detection and Repair (LDAR) programs are utilized in refineries and other industrial environments where volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are abundantly present. In principle, LDAR elements are designed to eliminate fugitive emissions by optimizing equipment monitoring, reporting, and maintenance. However, there are many more benefits of a properly implemented LDAR program worth knowing as an energy executive or facility employee.
This is one of the most important benefits of a well-maintained LDAR system. With the proper LDAR elements in place, facilities can dramatically reduce their fugitive emissions by expediting repair processes. Various leak detection equipment and techniques, such as Method 21, OGI, and FIDs, are used to quickly find compromised equipment and implement resolutions before the complications worsen. Additionally, LDAR programs include extensive record-keeping systems that often anticipate fugitive emissions and allow technicians to make repairs before complications ever arise.
Refineries and other industrial settings where VOCs are present are hazardous workplace environments. VOC emissions exposure can negatively impact your health and well-being, from headaches and coordination issues to chronic kidney and central nervous complications. With a well-run LDAR program in place, these dangerous environments become much safer settings for all working individuals. Primarily, leak detection equipment can alert employees to serious toxic leaks and give them time to exit the area safely. Additionally, LDAR monitoring programs help reduce fugitive emissions that reach the public, creating safer and cleaner environments for entire communities.
Did you know that implementing an effective LDAR program can actually save your business money? LDAR programs with optimized detecting and repairing capabilities can dramatically reduce a refinery’s overall maintenance expenses. Plus, these same elements limit product loss due to fugitive emissions. Finally, maintaining a solid LDAR system overall ensures compliance with environmental regulations and prevents fines and penalties.
Compliance with environmental and emissions regulations doesn’t just save your business from fines and penalties; it also enhances the company’s reputation as an eco-conscious and empathetic brand. Refining industries are constantly under the scrutiny of investors, regulators, and the public. Maintaining a solid LDAR program can boost your standing across these groups and lead to more business success.
An underrated benefit of maintaining a well-run LDAR system is the ability to authorize self-audits on your refinery instead of relying on government agencies and EPA inspectors. In fact, the EPA encourages businesses to conduct their own inspections every three years to save costs—both for you and the EPA—and expedite solutions for compliance issues. You can avoid EPA visits simply by implementing a proper LDAR program and actively monitoring its condition.
These are just some of the benefits of a properly implemented LDAR program—contact our friendly team at LDARtools to learn more about setting up effective Leak Detection and Repair today! Additionally, ensure your facility has the best leak detection equipment by checking out our selection of quality gear. Our flame ionization detector products are perfect for maintaining Method 21 detection techniques.
Leak detection is an essential part of environmental compliance in many industries, and complying with regulations can be challenging. Method 21 is a commonly used EPA method for leak detection, and there are instruments available to help comply with the method, such as the phx42 FID analyzer, also commonly known as a Toxic Vapor Analyzer or TVA*. In this blog post, we will compare the requirements of Method 21 to the capabilities of the phx42 instrument.
*This is a misnomer, but also a term the industry has accepted to describe portable FIDs.
Before we dive into the comparison, it’s worth mentioning which CFR parts require inspections done by Method 21. Method 21 is required by a number of EPA regulations, including, but not limited to:
The detector type is crucial in leak detection, as it determines the compounds the instrument can detect. Method 21 requires that the VOC instrument detector responds to the compounds being processed. Detector types that meet this requirement include catalytic oxidation, flame ionization, infrared absorption, and photoionization. The phx42 uses a flame ionization detector (FID), which detects hydrocarbons by measuring the ionization produced by a flame in contact with a sample gas. The FID is highly selective to hydrocarbons and has a low detection limit. Compared to other detector types, the FID is easy to use, reliable, and cost-effective.
Accurate measuring is essential in leak detection to ensure that leaks are detected at the correct concentration. Method 21 requires that the instrument is capable of measuring the leak definition concentration specified in the regulation. The phx42 has an accurate range of 0 – 100,000 ppm, which meets this requirement. This accuracy is due to the sensitivity of the FID, which is capable of measuring low concentrations of hydrocarbons.
The readability of the instrument meter scale is critical in leak detection to ensure that leaks are detected accurately. Method 21 requires that the scale of the instrument meter is readable to ±2.5 percent of the specified leak definition. The phx42 displays one tenth of 1 ppm, which meets this requirement. This readability is due to the high sensitivity of the FID, which allows for accurate measurement of low concentrations of hydrocarbons.
The flow rate of the instrument is essential in leak detection to ensure that the detector is supplied with a constant flow of sample gas. Method 21 requires that the instrument is equipped with an electrically driven pump to ensure that a sample is provided to the detector at a constant flow rate of 0.1 to 3.0 liter per min. The phx42 uses pump throttling to maintain a constant flow rate of 0.3 liters per min regardless of probe length and partial filter obstruction, which meets this requirement. This flow rate is essential for efficient leak detection and ensures that the FID is supplied with a constant flow of sample gas.
The probe size is crucial in leak detection to ensure that the instrument can access the areas where leaks may occur. Method 21 requires that the instrument is equipped with a probe or probe extension for sampling not to exceed 6.4 mm (1/4 in) in outside diameter, with a single end opening for admission of sample. The phx42 uses a 0.225 inch metal probe tip, which meets this requirement. This probe size is essential for accessing tight spaces where leaks may occur.
Safety is a significant concern in leak detection, as the process may involve explosive gases. Method 21 requires that the instrument is intrinsically safe for operation in explosive atmospheres as defined by the National Electrical Code by the National Fire Prevention Association or other applicable regulatory code for operation in any explosive atmospheres that may be encountered in its use. The instrument shall, at a minimum, be intrinsically safe for Class 1, Division 1 conditions, and/or Class 2, Division 1 conditions, as appropriate, as defined by the example code. The instrument shall not be operated with any safety device, such as an exhaust flame arrestor, removed. The phx42 has been certified intrinsically safe for Class 1 Division 1 Groups ABCD Temperature Rating T4. Documentation of this certification can be found on LDARtools.com.
When it comes to leak detection, complying with EPA regulations can be challenging. Method 21 is a commonly used EPA method for leak detection, and the phx42 instrument is an efficient tool for complying with the method. By comparing the requirements of Method 21 to the capabilities of the phx42 instrument, we can see that the phx42 meets or exceeds the requirements for detector type, measuring accuracy, readability, flow rate, probe size, and intrinsic safety. Whether you work in the oil and gas industry or petroleum refineries, the phx42 instrument is a reliable solution for meeting EPA regulations for leak detection.

Managing a successful emissions control program at your petroleum facility is no easy task, especially with the endless list of rules and regulations specific to this industry. Read this guide on understanding LDAR requirements for refinery operations to ensure better compliance and overall business performance.
Before we dive into specific LDAR requirements, it’s important to understand which governmental bodies and organizations actually set these regulations. The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) creates and enforces sweeping emissions standards for refineries, along with local jurisdictions and Department of Environmental Protection (DEP) branches. However, a large portion of U.S. refineries self-enforce LDAR requirements equal to or greater than those from the EPA, DEP, and others.
Independent auditing and self-reporting help identify and rectify compliance issues faster and more effectively than third parties. Furthermore, it reduces costs for both governmental agencies and refineries themselves. Of course, LDAR programs are only effective if you enforce and meet specific requirements.
There are three main elements to all LDAR programs: identification, monitoring, and repair. Notably, LDAR rules and regulations impact all of these elements to some extent. For example, leak identification requirements range from tagging standards to survey best practices, including the importance of a coded equipment labeling system and compliant action plans. Leak monitoring requirements impact the frequency of audits and equipment inspections.
Some jurisdictions enforce upwards of three visits a year, while other refineries simply conduct these reports independently. Finally, repair requirements include any operation related to fixing leaks and related emissions complications, such as repair expenses and detailed records of incidents. As you can see, LDAR requirements are far-reaching and impact your entire operation.
So, why is it so important for refineries to practice compliance when managing their LDAR systems? For starters, LDAR programs reduce health and environmental hazards associated with toxic emission leaks. Thanks to dedicated technicians, advanced software, and highly sensitive monitoring equipment, refineries can identify and rectify significant issues faster than ever in human history.
However, these innovations are for naught without compliance with EPA standards and self-regulation. Ultimately, these protections are in place to prevent toxic exposure in your workforce and contamination and pollution impacting surrounding ecosystems and communities.
Understanding LDAR requirements for refinery operations ensures better protections for individuals and the environment, enhanced operational performance, and overall better working conditions for everyone. Stock up on helpful LDAR equipment from our team at LDARtools, including advanced software and FID meter products.
1102 Dickinson Ave.
Dickinson, Texas 77539
USA
Telephone: +1 (877) 788-1110
Fax: +1 (866) 385-9142
Mo-Th: 8:00AM – 5:00PM
Fr: 8:00AM – 3:00PM
After Hours: By Appointment
© 2026 LDARtools. All rights reserved.
