
-
- Wednesday, December 24, 2025
- Thursday, December 25, 2025
- Thursday, January 1, 2026
Have a blessed and safe holiday.
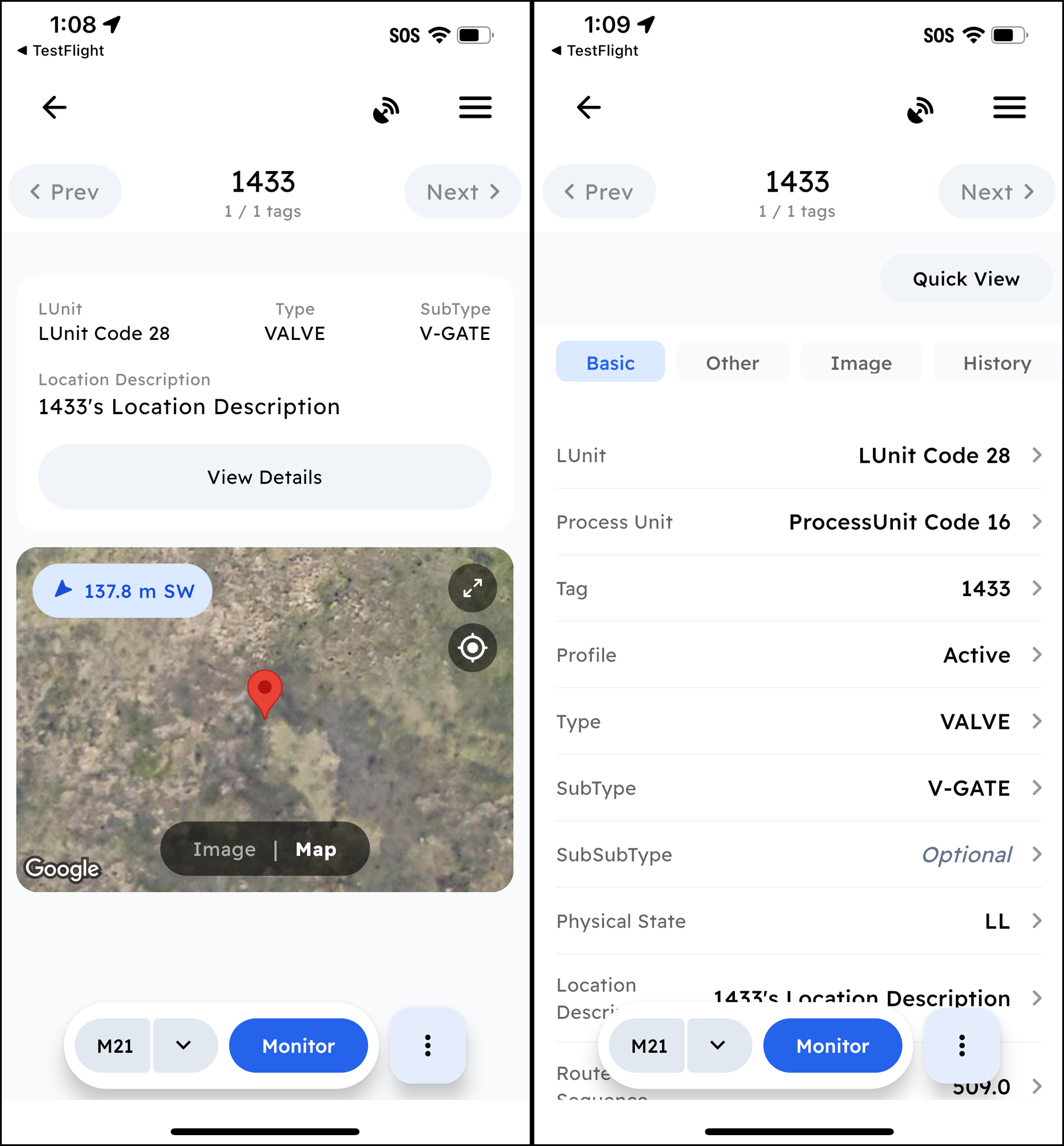
The updated Chateau Mobile application is now available. The redesign features a modernized interface, improved performance, and simplified field inspection workflows.
Redesign Highlights
Key features of the redesign include:
-
Improved filtering tools for managing components within a tour.
-
A simplified, faster, and more intuitive Post-Inspection workflow.
-
Add via Photo: Technicians can now take a photo of multiple components and quickly create and tag new components directly from the image.
-
Faster device registration with QR code scanning.
-
Increased performance across all devices.
-
iOS Support: Chateau Mobile is now available for iOS devices. Please note that Bluetooth analyzer connections are not currently supported on iOS. Users must manually enter PPM values for M21 inspections on iOS.
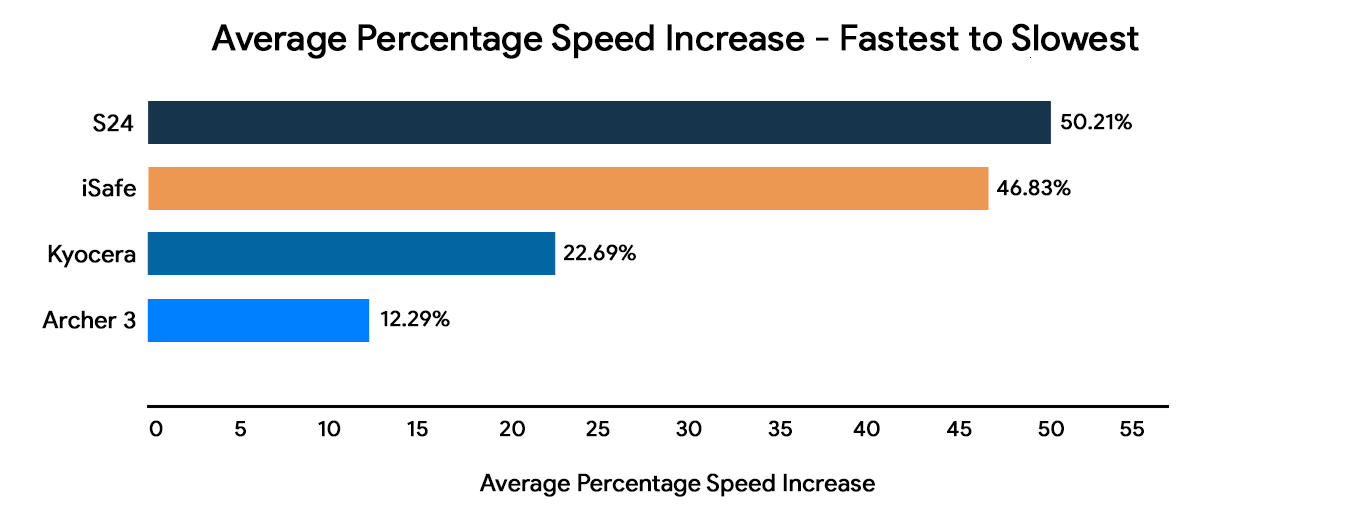
Performance Improvements
When compared to the previous version of Chateau Mobile, there are substantial speed improvements across the most frequently used handhelds:
New Training Material
Training resources for the new Chateau Mobile redesign are available. We recommend that you have your Technicians watch the applicable “What A Technician Needs to Know” tutorial video before installing the new App.
-
Chateau Mobile Tutorials
-
Additional tutorial videos are available here.
-
For an offline training tool, download the revised Chateau Mobile Training Manual.
Updating Chateau Mobile (Google Play)
Depending on your Google account, Chateau Mobile may not automatically update. Please follow the steps below to update your handheld so you can take advantage of this redesign. Please check in your data before updating Chateau Mobile.
- In the Google Play Store, click the circular profile button in the upper-right portion of the screen.
- Select Manage Apps & Device.
- Under the Manage tab, filter by “Installed” and “Updates Available.”
- Click Update.
LDARtools will be closed Monday September 1, 2025 in recognition of Labor Day.
We will be conducting normal business operations Friday August 29 and Tuesday September 2.

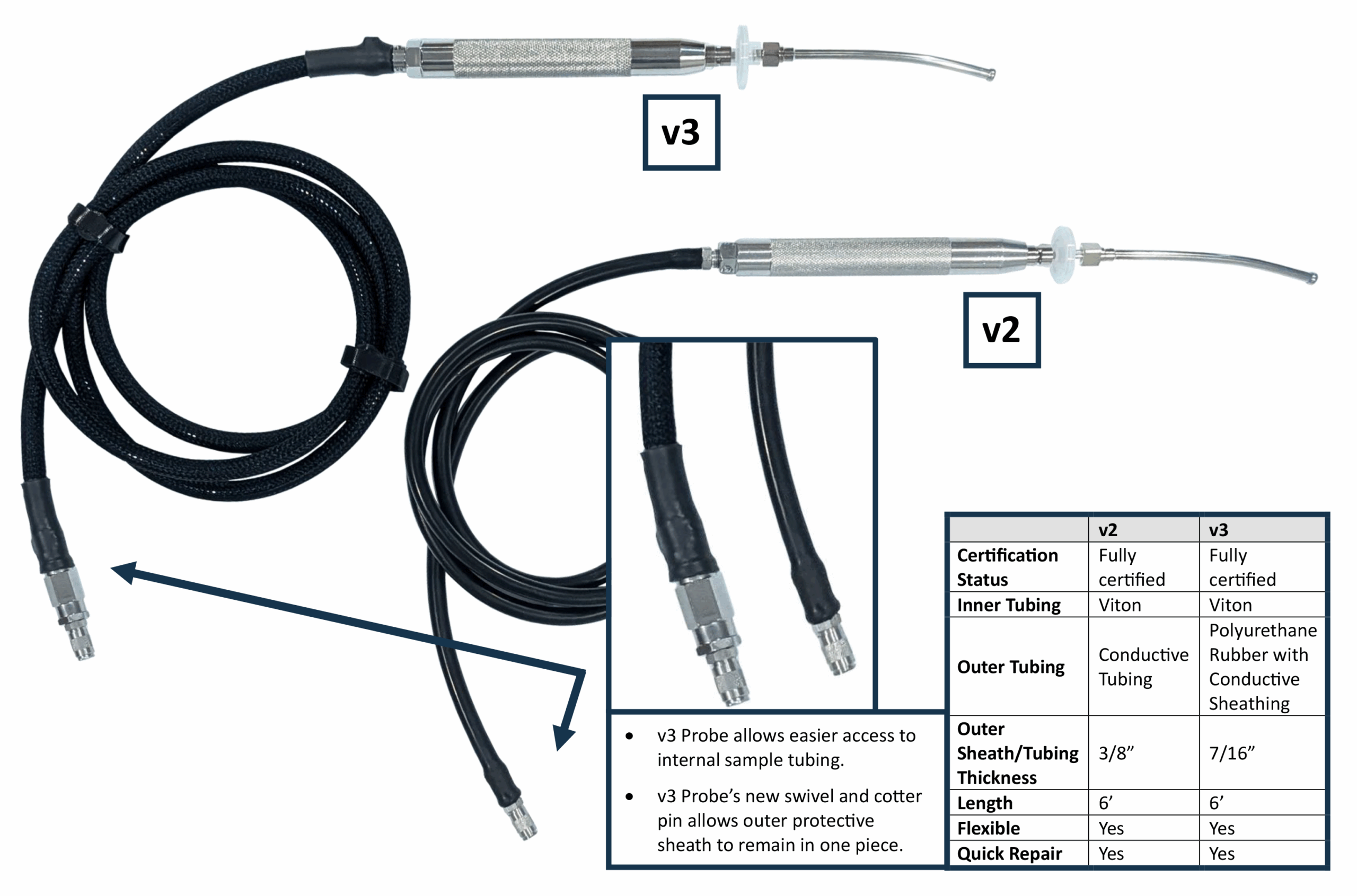
We’re excited to unveil the latest evolution in our probe lineup — a next-generation design that’s built to outperform and outlast.
- Stronger Than Ever: Engineered with rugged materials, this probe is tougher and more durable than V2, making it ready for the harshest conditions.
- Simplified Maintenance: Say goodbye to downtime. Our new design is easier to repair than previous models, with streamlined access to the sample tubing.
- Field-tested and tech-approved, this model has already proven itself where it counts — in real-world use.
This is the probe you’ve been waiting for.
v3 Probes will begin shipping with new phx42s purchased after 7/15/25. If you currently have an older model and would like to upgrade, contact sales@ldartools.com.
The future of durability is here.
For repair procedures, scan below or click here.

In honor of Memorial Day, our Warehouse and Support will be closed Monday, May 26, 2025. We will resume normal business operations on Tuesday, May 27, 2025.


At a time when price increases are becoming more common, a price reduction on a quality product is always a welcoming breath of fresh air. As of February 7, 2025, we have reduced the price of the SpanBox Lite 530 from $4,198.69 to $3,653.50. This reduction is a result of the recent retirement of the SpanBox Lite 510; compensation for reducing the number of products available in our SpanBox5 series.
Paired with our Cal5.0 software, the SpanBox Lite 530’s support for five calibration gases and up to three phx42s ensures you receive the same experience as with the Lite 510, but with the added convenience of being able to calibrate multiple phx42s.
For more information on the SpanBox5 and Cal5.0, please visit our SpanBox5 page, or contact our Sales team at sales@ldartools.com.
We here at LDARtools are standing by to help create an LDAR system that works for you, and as always, we appreciate your business.


